There are a staggering number of people in the U.S. suffering from hoarding behavior. Individuals engage in excessive accumulating or have difficulty letting go of items, sometimes so severe that it interferes with normal activities of daily life. Rooms are no longer usable for their intended purpose, we see dining rooms cluttered with belongings not meals or tubs holding clothes not bathwater. Statistics estimate that 15 million people are dealing with this issue. In Philadelphia, the estimate is 31,000 -77,000.
A cleanout is the method most municipalities use to deal with hoarding. Reducing the volume of clutter to safer levels is thought to alleviate the problem and support the person. The reality is, without treatment and support for the individual, the rate of recidivism after a cleanout is nearly 100%. With the high cost of cleanouts and low rate of return, cities are beginning to pay attention to research findings.
Thanks to the research of doctors Frost, Steketee, Tompkin and Tolin, we are now understanding that cleanouts are “stuff-centered” and don’t address the issues buried below the surface. Simply removing clutter without addressing the underlying issues illuminates the reasons for high recidivism rates after cleanouts. This research is stimulating new intervention models. Being “people-centered” is the common theme. They each involve the person with hoarding behavior as key to the solution. Given that 92% of individuals diagnosed with Hoarding Disorder also have another co-occurring disorder, there is no one set solution.
The work is personalized and takes keen listening skills, creativity, flexibility, patience, and lots of compassion. Instead of focusing solely on the volume of clutter, a spotlight shines on the safety and well-being of the individual while working to reframe old thoughts and beliefs to reduce the dependence on acquiring and saving. There is no magic pill. Everyone involved understands this disorder has deep roots; the process takes time and relapses are as common as seen with over eating or drinking.
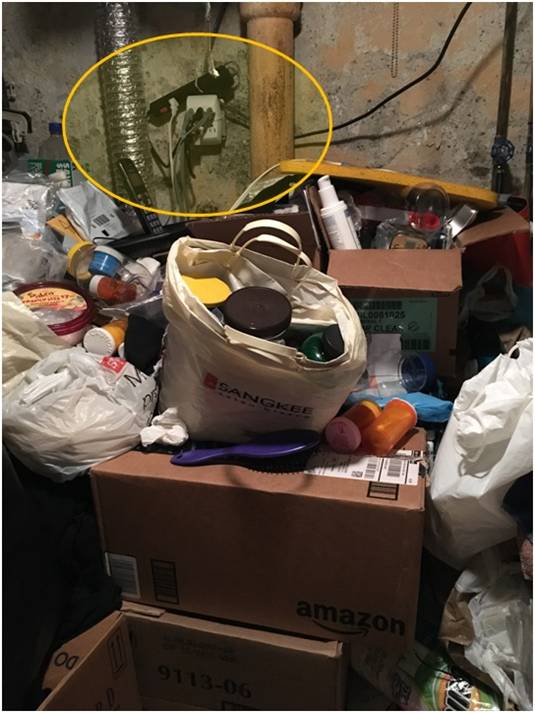

One of the new models is Harm Reduction (HR). Its goal is to reduce the risks associated with hoarding. Instead of talking about the “stuff” to get rid of, it asks the question, “How do we keep you safe in your home and maintain clear access for emergency staff and equipment if the need ever arises?” The (HR) process provides a support person that works with the individual identifying key health and safety concerns in the home. They also serve to document goals to alleviate the issues. From this information, they design and implement a strategy to address these issues over time.
One such organization that has adopted this (HR) model is the Philadelphia Hoarding Task Force (PHTF). The Task Force is a coalition of organizations that seek to improve outcomes for people who hoard while balancing the rights of the individual with the health and safety needs of the community. PHTF is introducing service providers to this model as a way to circumvent the costly and catastrophic consequences often seen with cleanouts and instead, create favorable long lasting results.
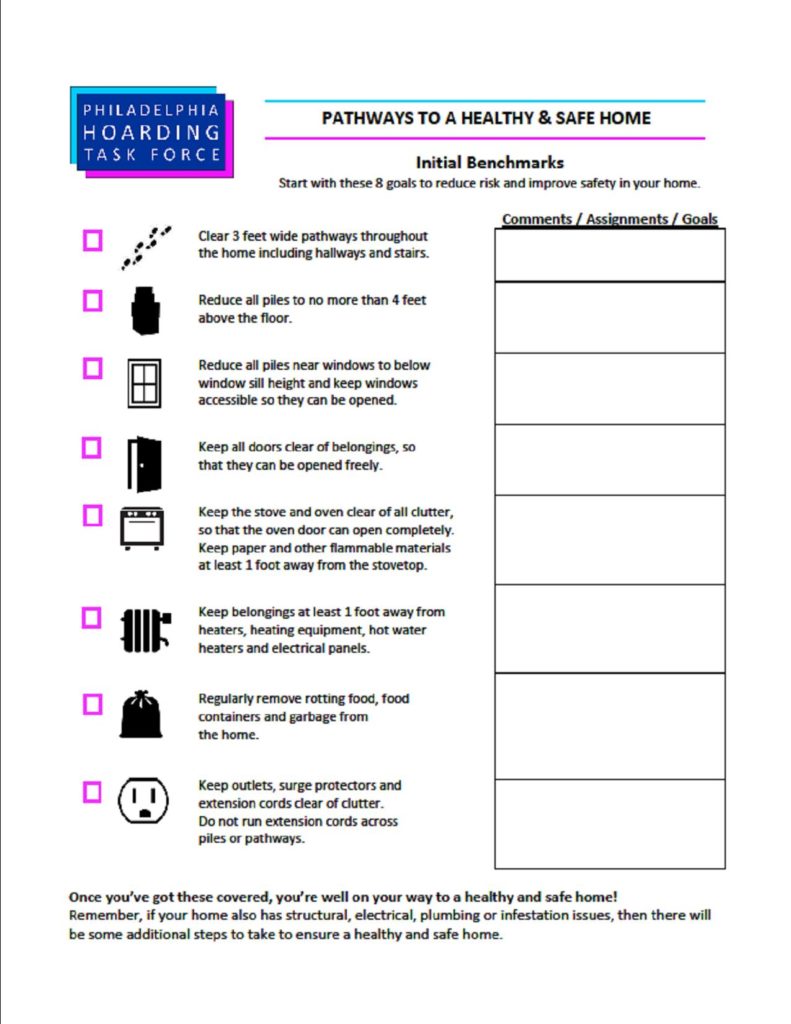
Consulting with its members from Licensing and Inspections and the Fire Department, PHTF has come up with 8 Benchmarks to follow to create healthier, safer homes. These benchmarks provide specific measureable goals that support, guide, and unify everyone involved. They address potential hazards regarding fire, tripping, limited access in or out of the home for the individual, emergency personnel and their equipment, avalanches, health issues and infestation. The benchmarks are as follows: